The abacus – the oldest calculating machine
Where does the term “abacus” come from?
The term “abacus” has a meaning not only in mathematics, but also in architecture. There it stands for a column top plate, a board-like upper member of the capital. In other words, a “square plate at the head of columns. But it also has the meaning ” of a “command staff at temples” (in: Wiktionary). However, all this is not meant in the following. Here it concerns the “abacus”, which can be called probably rightly the oldest calculating machine of mankind. How to use an abacus?
According to Duden, the word “abacus” comes from the Greek, from “abákion”, and stands for arithmetic or game board of antiquity. If we go back to Latin, it comes from the word “abacus”.
Of course, the word abacus also exists in German sign language. To see it, please click here:
If it goes after the Duden, then as plural of the word “the abacus” “the abacus” is to be used (Duden, 1999). This sounds strange at first, but it is so. I stick to the plural formation. Since the Duden is no longer binding for the German language, the plural formation 1 in the Wiktionary should also be mentioned here. Here the plural 1 is namely “the Abaki” and obviously derived from Latin, as well as the word “abakus”. This makes sense in my opinion. The plural 2 is therefore “the abacuses” (in: Wiktionary).
The abacus has practically no meaning as a calculating device in Europe today. Electronic pocket calculators have replaced it. However, there are various abacuses for learning basic arithmetic operations for children, especially in pre-school and primary school age. In Asian, but also Arabic countries, arithmetic with the abacus is still learned in special arithmetic schools. It has been proven that it promotes the ability for quick and secure mental arithmetic even with very large numbers.
The historical roots of the abacus
The historical roots of the abacus probably lie in Asia, because “already around 1100 B.C. this ‘calculating machine’ was known in China” (Microsoft ENCARTA Encyclopedia PLUS 99). Originally, in this ancient advanced civilization, number rods were placed on printed tablets. Later, pierced counting stones were slid back and forth on sticks. This was already the basic form of an abacus. These stones now had a clear, always constant order, a place value system. They could be moved according to one’s own idea, but better according to a uniform calculation rule. Other sources assume that the abacus was developed by the Babylonians (National Geographic, November 2010, page 32): https://argoprep.com/blog/k8/abacus/.
The Chinese abacus came to Japan and was further developed into the soroban. The Indians also used similar things for arithmetic, namely so-called “dust tables”. The Babylonians already had tables for calculating with the multiplication tables around 1350 BC. By the way, why shouldn’t mankind in their advanced civilizations of that time make parallel and independent inventions of abacus or calculating boards? By the way, also the Maya knew the abacus. They called it Nepohualtzintzin. Whether it made the leap across the Atlantic, or was invented in parallel, certainly still needs clarification.
The cultural basis for the abacus used today in Europe is probably to be found in ancient Greece. The unique find of the “Salaminic Arithmetic Table” (National Museum in Athens), represents such a mathematical primitive device from the Greek cultural sphere. It was made of white marble and its age is estimated to the third century BC. On this historical abacus a division into fields is achieved by horizontal and vertical lines. Further one finds on it Greek number signs. On this arithmetic board it was possible to move loose arithmetic blocks back and forth. Here was a clear mathematical order, which could be used according to fixed rules. A miscalculation became improbable. There must have been something similar to the “Salaminic arithmetic table” also as an arithmetic table. The Greeks called their version of the abacus “abákion”.
“In ancient times … the Romans used a sand-covered wax tablet, a marked plate, or a notched tablet or plate” for arithmetic (Microsoft ENCARTA Encyclopedia PLUS 99). It is known from finds that they used hand abacuses made of clay for their arithmetical calculations. The Roman name “abacus” was used for this, the eponym of all modern abacuses.
The illustration of an ancient Roman hand abacus shows seven rows of four beads at the bottom and one at the top. Between the two rows of slits in the vertical you can find Roman numerals. It was probably used in a similar way to a Japanese abacus (soroban). With this Roman abacus, even fractions were possible. The beads of the two additional right rows stand for whole, half, quarter and third ounces. The similar construction of the Roman abacus with the Greek and Chinese abacus of that time is obvious. But there is especially an astonishing similarity with the Japanese soroban. This is probably an ancient technology transfer from the Asian to the Southeast European area, perhaps due to wars, trade relations or travelers.
With these ancient abacuses, one could safely handle all calculations in the commercial or statesmanlike field at that time. It should be remembered that it was not only a matter of actual arithmetic. The known world at that time was still far away from a uniform currency or measurement system. Just such conversions, therefore, were common in all places. In the old Rome, with their Roman numbers, one knew no “zero” and thus also no units, tens or hundreds etc.. The balls or calculating stones, Latin “calculi”, represented a certain number only by their position. Consequently, a place value system is used as a basis, which, however, is to be understood differently than our today’s decimal system.
“In medieval England, a simplified version of the abacus was used. It consisted of a board divided into squares representing the positions of the tiles. To calculate, coins, buttons, stones or other small objects were moved. The checkered tablecloth, from which the name exchequer comes, was originally a device for arithmetic like the divided table” (Microsoft ENCARTA Encyclopedia PLUS 99).
The famous German arithmetic master, Adam Riese, described the use of arithmetic boards in his work “Rechenbuch auff Linien und Ziphren in allerlei Handthierung / geschäfften und Kaufmanschafft”. His merit lies in particular in having popularized arithmetic in the decimal system commonly used today in German-speaking countries. It originated in the Arabic world and was perfected here. E.g. the digit “zero”, originated in the Indian area, was cleverly used for arithmetic. The Arabic origin was exactly the reason for the Catholic Church to dismiss it as pagan. Accordingly, the church at that time worked very much against the introduction of this form of arithmetic. However, especially the merchants of Europe quickly recognized the enormous advantage of this Arabic way of calculating, because until then they had been calculating in the Roman system. This was very cumbersome, even if one used an abacus or an abacus. Methodically, Adam Riese used a new type of abacus for his Arabic calculation. Perhaps the basis of all European abacus forms?
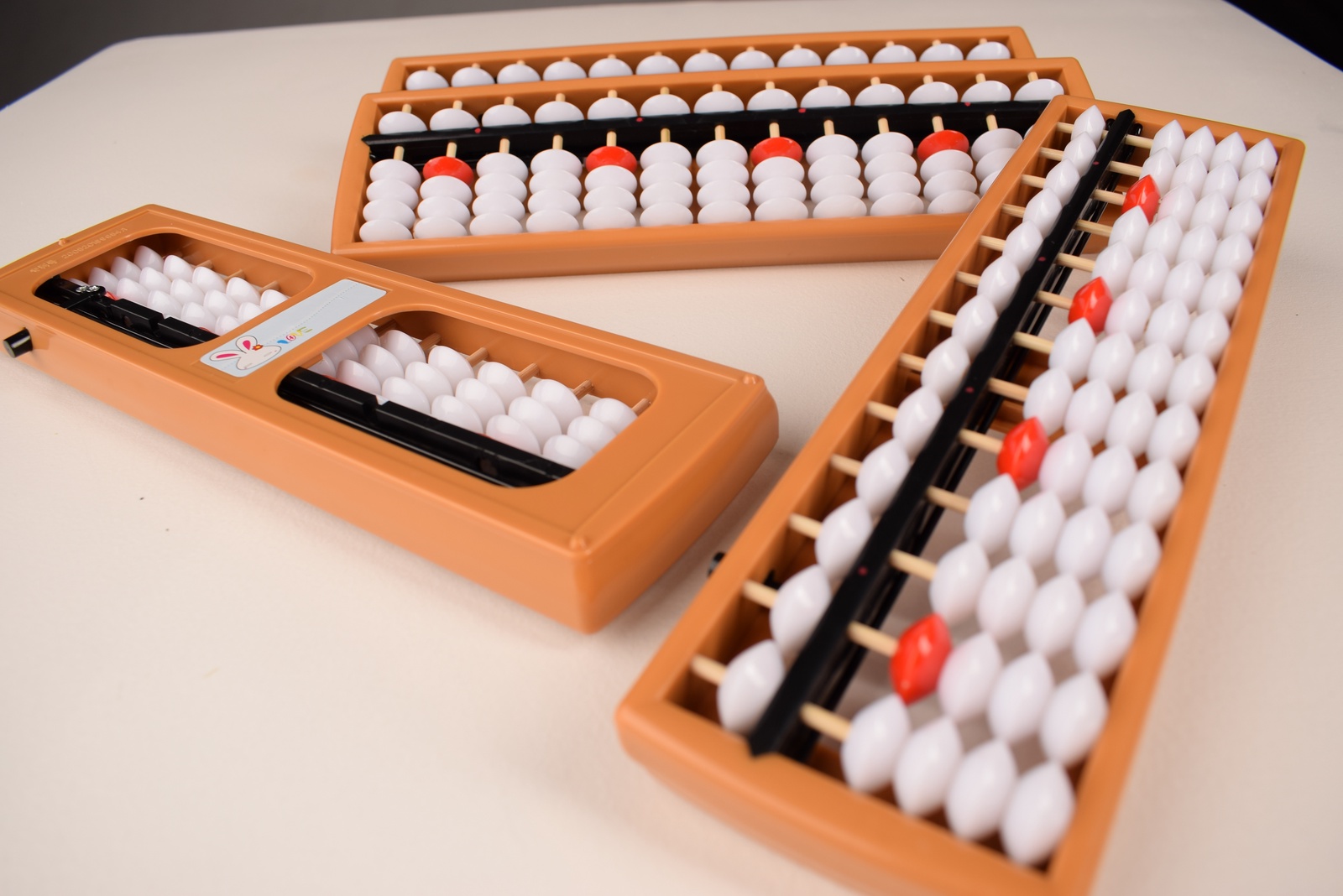
The abacus still allows complicated arithmetic operations today. Actually, it is still very simple in construction. It consists of a frame with balls or stones, called “beads”, which are threaded on rods or wires or guided in slots. It was used extensively in our country until the 16th century. Today it is only used in Asia, especially in China, rather in small stores. In addition to the four basic arithmetic operations, it is also possible, among other things, to draw roots with the help of an abacus. Addition and subtraction of large numbers are probably the absolute strengths of an abacus, even compared to a modern pocket calculator.
A definition of the term is important to me. An abacus is not a slide rule! With an abacus you calculate in a place value system. Today this is usually the decimal system (10s system). The mathematical basis of a slide rule is the calculation with logarithms.